The “1, 2, 3” cache clear method in Linux refers to clearing different types of caches managed by the operating system. Each cache type is managed differently and cleared by writing a specific value to the file /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches.
Cache Types:
- PageCache (Value:
1):- PageCache stores file contents that are cached in memory to reduce disk I/O.
- Dentries and Inodes (Value:
2):- Dentry is a cache of directory entries, and inodes store file metadata.
- PageCache + Dentries + Inodes (Value:
3):- Clears both PageCache and Dentry/inode caches.
Steps to Clear Cache with Examples:
1. Check Current Memory Usage
Use the free -h command to view current memory and cached memory:
free -h
Look under the “buff/cache” column to see the cache usage.
2. Clear Cache
Use the following commands to clear caches. Root privileges are required, so prefix with sudo:
Clear PageCache:
sudo sh -c "echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches"
Clear Dentry and Inode Cache:
sudo sh -c "echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches"
Clear Both PageCache and Dentry/Inode Cache:
sudo sh -c "echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches"
3. Check Memory Usage Again
Run the free -h command again to verify that the cache has been cleared.
Example Workflow:
- Check Memory Before Clearing:
free -hOutput:total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 15Gi 4.0Gi 2.0Gi 0.5Gi 9Gi 10Gi Swap: 2Gi 0B 2Gi - Clear All Caches (PageCache, Dentries, and Inodes):
sudo sh -c "echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches" - Check Memory After Clearing:
free -hOutput:total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 15Gi 4.0Gi 7.0Gi 0.5Gi 4Gi 11Gi Swap: 2Gi 0B 2Gi
Notice how the “buff/cache” column decreases.
Best Practices
- Clearing caches isn’t typically necessary because Linux uses unused memory to cache files and automatically clears it when needed.
- Use this method only for debugging or specific needs (e.g., testing performance under no cache conditions).
Would you like to try this on your system now? Let me know if you need additional help!
Let’s break down PageCache, Dentries, and Inodes with simple explanations and commands you can use on your Ubuntu system to see how they work.
1. PageCache
- What it is:
- PageCache stores file data read from disk in memory to speed up future reads.
- If a file is accessed again, the system reads it from memory instead of the slower disk.
- Example:
- Create a Large File:
dd if=/dev/zero of=testfile bs=1M count=100This creates a filetestfileof 100 MB size. - Clear Cache:
sudo sh -c "echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches" - Read the File (Populates PageCache):
time cat testfile > /dev/nullThe first read is slow because it loads data from disk. - Read the File Again (From PageCache):
time cat testfile > /dev/nullThe second read is faster as it fetches data from memory (PageCache). - Verify Cache Usage: Check memory usage using:
free -h
- Create a Large File:
2. Dentries
- What it is:
- A dentry (directory entry) cache stores metadata about directories, such as filenames and their locations in the filesystem.
- This speeds up directory traversals and file lookups.
- Example:
- Clear Cache:
sudo sh -c "echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches" - List a Large Directory (Populates Dentry Cache):
ls -R /usr > /dev/null - List the Directory Again (From Dentry Cache):
time ls -R /usr > /dev/nullThe second run will be faster because the directory structure is cached in memory.
- Clear Cache:
3. Inodes
- What it is:
- An inode is a data structure storing metadata about a file (e.g., permissions, owner, size).
- Inode caching stores this metadata to reduce disk reads.
- Example:
- Find Inodes Used by the System:
df -iThis shows the inode usage for each mounted filesystem. - Create Many Files (Populates Inode Cache):
mkdir testdir for i in {1..10000}; do touch testdir/file$i; done - Clear Cache:
sudo sh -c "echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches" - List Files (Rebuilds Inode Cache):
time ls testdir > /dev/null - List Files Again (From Inode Cache):
time ls testdir > /dev/nullThe second run will be faster due to inode caching.
- Find Inodes Used by the System:
Summary of Commands:
free -h: Check memory usage (PageCache in “buff/cache”).df -i: Check inode usage for filesystems.echo [1|2|3] > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches: Clear caches.
The command dd if=/dev/zero of=testfile bs=1M count=100 is a Linux command used to create a file filled with zeros. Here’s a breakdown of each part:
Command Breakdown:
dd:- A low-level command-line utility used for copying and converting data between files or devices.
if=/dev/zero:ifstands for “input file.”/dev/zerois a special file in Linux that produces a continuous stream of null bytes (zeros).
of=testfile:ofstands for “output file.”testfileis the name of the file where the data (zeros) will be written.
bs=1M:bsstands for “block size.”- This sets the size of each block of data to 1 Megabyte (MB).
count=100:- Specifies the number of blocks to copy.
- In this case, 100 blocks of 1 MB each.
What the Command Does:
- It writes 100 MB (1 MB × 100 blocks) of zero-filled data to a file named
testfile.
Example Output:
When you run the command, you’ll see something like this:
100+0 records in 100+0 records out 104857600 bytes (105 MB) copied, 0.123456 s, 847 MB/s
This means:
100+0 records in: 100 blocks read from the input file (/dev/zero).100+0 records out: 100 blocks written to the output file (testfile).104857600 bytes: Total bytes written (100 MB).0.123456 s: Time taken to execute the command.847 MB/s: Write speed.
Verify the File:
- Check the file size:
ls -lh testfileYou should see the size as100 MB. - Inspect the file contents:
hexdump -C testfile | headThis will display the file’s contents in hexadecimal format, and you’ll see it filled with00(zeros).
Why clearing dentries does not affect memory a lot
The behavior you’re observing can be explained by how Linux handles PageCache and Dentries/Inodes caching.
Key Points:
- PageCache (Cleared with
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches):- Clearing PageCache removes cached file data but does not clear dentries and inodes.
- If you only clear the PageCache, Linux has to read file contents from disk, but dentry and inode information might still be available in memory.
- Dentries and Inodes (Cleared with
echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches):- Clearing dentry and inode caches removes directory structure and file metadata information from memory.
- If dentry and inode caches are cleared, listing directories or performing file operations becomes slower because the system must rebuild this information by reading from disk.
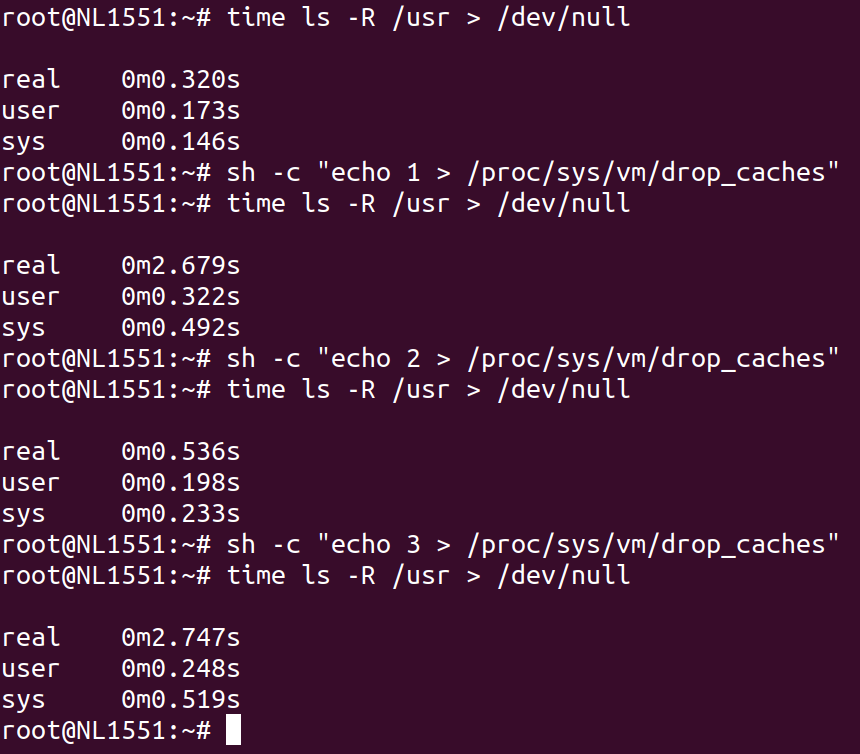
Your Test Results:
- Before Cache Clear:
- The first
ls -Rcommand runs quickly (0.343s) because both PageCache and dentry/inode caches are populated.
- The first
- After Clearing PageCache:
- After running
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches, the secondls -Rcommand takes significantly longer (2.756s) because:- PageCache is cleared, so file contents must be reloaded from disk.
- However, dentries and inodes are not cleared, so some metadata is still available.
- After running
Why It Still Takes More Time:
The additional time comes from the fact that:
- After clearing the PageCache, the system has to read the file contents (or parts of the directory structure) from disk, which is slower than fetching them from memory.
- Even though dentries and inodes are still in memory, they depend on PageCache for efficient access to file content. So the system has to do extra work to populate the PageCache again.
- Directory traversal involves a combination of file metadata (dentries/inodes) and directory file contents (loaded via PageCache). Clearing just the PageCache impacts this process.
Solution to Test Dentry Cache Impact:
To focus solely on dentry and inode caches, you need to clear them explicitly with:
sh -c "echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches"
Then rerun:
time ls -R /usr > /dev/null
You’ll notice that this run will also take longer compared to when the dentry cache is intact, but the pattern will differ from clearing the PageCache.
Suggested Workflow to Understand All Cache Impacts:
- Baseline:
time ls -R /usr > /dev/null - Clear PageCache:
sh -c "echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches" time ls -R /usr > /dev/null - Clear Dentries and Inodes:
sh -c "echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches" time ls -R /usr > /dev/null - Clear Both PageCache and Dentries/Inodes:
sh -c "echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches" time ls -R /usr > /dev/null
This should give you a clear understanding of how each type of cache contributes to performance.