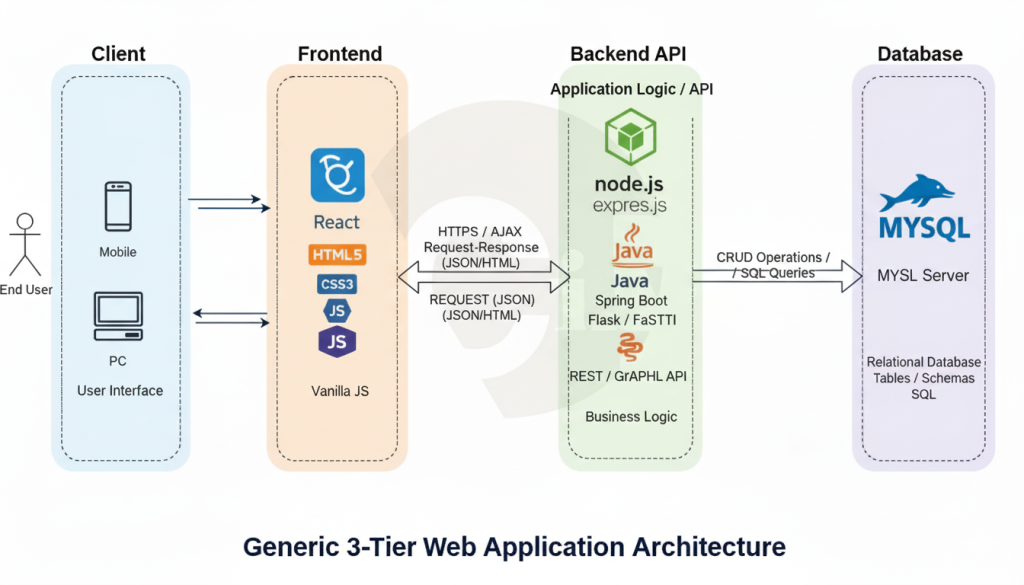
Programming Fundamentals Curriculum
A comprehensive guide covering JavaScript, Java, Python, and Node.js
Table of Contents
- Basic Syntax & Variables
- If-Else Statements
- For Loops
- Arrays
- Array of JSON Objects
1. Basic Syntax & Variables
Concept Overview
Variables are containers that store data values. Each programming language has its own syntax for declaring and using variables.
Syntax Comparison
JavaScript:
// Variable declaration
let name = "John";
const age = 25;
var city = "New York"; // older syntax
// Data types
let number = 42;
let text = "Hello World";
let isActive = true;
let items = null;
Java:
// Variable declaration with type specification
String name = "John";
final int age = 25; // final = constant
int number = 42;
boolean isActive = true;
Python:
# Dynamic typing - no need to specify type
name = "John"
age = 25 # Numbers can be changed later
number = 42
text = "Hello World"
is_active = True # Note: True/False capitalized
Node.js:
// Same as JavaScript (Node.js runs JavaScript)
const name = "John";
let age = 25;
console.log(`Hello ${name}, you are ${age} years old`);
Example 1: Basic Calculator
JavaScript:
let num1 = 10;
let num2 = 5;
let sum = num1 + num2;
console.log("Sum: " + sum);
Java:
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 5;
int sum = num1 + num2;
System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);
}
}
Python:
num1 = 10
num2 = 5
sum = num1 + num2
print(f"Sum: {sum}")
Example 2: User Profile
JavaScript:
const firstName = "Alice";
const lastName = "Johnson";
let age = 28;
let fullName = firstName + " " + lastName;
console.log(`Profile: ${fullName}, Age: ${age}`);
Python:
first_name = "Alice"
last_name = "Johnson"
age = 28
full_name = first_name + " " + last_name
print(f"Profile: {full_name}, Age: {age}")
Classwork 1: Personal Information
Create variables to store your personal information and display them:
- Full name (combine first and last name)
- Age
- Favorite color
- Current year
- Calculate birth year using current year and age
Classwork 2: Shopping Calculator
Create a program that calculates the total cost of shopping:
- Item price
- Quantity
- Tax rate (8%)
- Calculate total cost including tax
Classwork 3: Temperature Converter
Create variables to convert temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit:
- Celsius temperature
- Apply formula: F = (C × 9/5) + 32
- Display both temperatures
Assignments
Assignment 1: Student Grade Calculator Create a program that stores a student’s information and calculates their average grade:
- Student name
- Three subject scores (Math, Science, English)
- Calculate average
- Display student name and average grade
Assignment 2: Rectangle Area and Perimeter Write a program that calculates the area and perimeter of a rectangle:
- Length and width variables
- Calculate area (length × width)
- Calculate perimeter (2 × (length + width))
- Display all values with appropriate labels
Assignment 3: Time Converter Create a program that converts time:
- Total seconds as input
- Convert to hours, minutes, and remaining seconds
- Display in format “X hours, Y minutes, Z seconds”
Assignment 4: Simple Interest Calculator Calculate simple interest on a loan:
- Principal amount
- Interest rate (annual percentage)
- Time period (in years)
- Calculate simple interest = (P × R × T) / 100
- Display principal, interest, and total amount
Assignment 5: BMI Calculator Create a Body Mass Index calculator:
- Height in meters
- Weight in kilograms
- Calculate BMI = weight / (height × height)
- Display height, weight, and BMI with appropriate messages
2. If-Else Statements
Concept Overview
Conditional statements allow programs to make decisions based on different conditions. They execute different blocks of code depending on whether conditions are true or false.
Syntax Comparison
JavaScript:
// Basic if-else
if (condition) {
// code if true
} else if (anotherCondition) {
// code for another condition
} else {
// code if all conditions are false
}
// Comparison operators: ==, ===, !=, !==, <, >, <=, >=
// Logical operators: &&, ||, !
Java:
// Basic if-else
if (condition) {
// code if true
} else if (anotherCondition) {
// code for another condition
} else {
// code if all conditions are false
}
// Comparison operators: ==, !=, <, >, <=, >=
// Logical operators: &&, ||, !
Python:
# Basic if-else (note the indentation and colons)
if condition:
# code if true
elif another_condition:
# code for another condition
else:
# code if all conditions are false
# Comparison operators: ==, !=, <, >, <=, >=
# Logical operators: and, or, not
Example 1: Grade Classification
JavaScript:
let score = 85;
let grade;
if (score >= 90) {
grade = "A";
} else if (score >= 80) {
grade = "B";
} else if (score >= 70) {
grade = "C";
} else if (score >= 60) {
grade = "D";
} else {
grade = "F";
}
console.log(`Score: ${score}, Grade: ${grade}`);
Python:
score = 85
if score >= 90:
grade = "A"
elif score >= 80:
grade = "B"
elif score >= 70:
grade = "C"
elif score >= 60:
grade = "D"
else:
grade = "F"
print(f"Score: {score}, Grade: {grade}")
Example 2: Age Category
JavaScript:
let age = 17;
let category;
if (age < 13) {
category = "Child";
} else if (age < 20) {
category = "Teenager";
} else if (age < 60) {
category = "Adult";
} else {
category = "Senior";
}
console.log(`Age: ${age}, Category: ${category}`);
Java:
public class AgeCategory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 17;
String category;
if (age < 13) {
category = "Child";
} else if (age < 20) {
category = "Teenager";
} else if (age < 60) {
category = "Adult";
} else {
category = "Senior";
}
System.out.println("Age: " + age + ", Category: " + category);
}
}
Classwork 1: Number Checker
Write a program that checks if a number is:
- Positive, negative, or zero
- Even or odd (if not zero)
- Display appropriate messages
Classwork 2: Login System
Create a simple login system:
- Check if username is “admin” and password is “123456”
- Display “Login successful” or “Invalid credentials”
- Add a check for empty username or password
Classwork 3: Weather Recommendation
Based on temperature, recommend clothing:
- Below 0°C: “Wear heavy coat”
- 0-15°C: “Wear jacket”
- 16-25°C: “Wear light clothing”
- Above 25°C: “Wear summer clothes”
Assignments
Assignment 1: Traffic Light System Create a traffic light program:
- Input a color (red, yellow, green)
- Output the appropriate action (stop, caution, go)
- Handle invalid colors with an error message
Assignment 2: Discount Calculator Create a discount system based on purchase amount:
- $0-$99: No discount
- $100-$499: 5% discount
- $500-$999: 10% discount
- $1000+: 15% discount
- Calculate and display final amount
Assignment 3: Password Strength Checker Check password strength based on:
- Length (minimum 8 characters)
- Contains numbers
- Contains uppercase letters
- Display “Strong”, “Medium”, or “Weak”
Assignment 4: Leap Year Calculator Determine if a year is a leap year:
- Divisible by 4 AND (not divisible by 100 OR divisible by 400)
- Display whether the year is a leap year or not
Assignment 5: Grade Point Average Calculator Convert letter grades to GPA:
- A = 4.0, B = 3.0, C = 2.0, D = 1.0, F = 0.0
- Take multiple grades and calculate average GPA
- Display GPA with classification (Excellent, Good, Average, Poor)
3. For Loops
Concept Overview
For loops allow you to repeat a block of code a specific number of times or iterate through collections of data. They’re essential for processing multiple items efficiently.
Syntax Comparison
JavaScript:
// Traditional for loop
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
// For...of loop (for arrays)
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
for (let fruit of fruits) {
console.log(fruit);
}
// For...in loop (for object properties)
let person = {name: "John", age: 30};
for (let key in person) {
console.log(key + ": " + person[key]);
}
Java:
// Traditional for loop
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
// Enhanced for loop (for arrays/collections)
String[] fruits = {"apple", "banana", "orange"};
for (String fruit : fruits) {
System.out.println(fruit);
}
Python:
# For loop with range
for i in range(10):
print(i)
# For loop with list
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
# For loop with enumeration (index and value)
for index, fruit in enumerate(fruits):
print(f"{index}: {fruit}")
Example 1: Multiplication Table
JavaScript:
let number = 5;
console.log(`Multiplication table for ${number}:`);
for (let i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
let result = number * i;
console.log(`${number} × ${i} = ${result}`);
}
Python:
number = 5
print(f"Multiplication table for {number}:")
for i in range(1, 11):
result = number * i
print(f"{number} × {i} = {result}")
Java:
public class MultiplicationTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 5;
System.out.println("Multiplication table for " + number + ":");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
int result = number * i;
System.out.println(number + " × " + i + " = " + result);
}
}
}
Example 2: Sum Calculator
JavaScript:
let numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
let sum = 0;
console.log("Numbers:", numbers);
for (let number of numbers) {
sum += number;
console.log(`Adding ${number}, running total: ${sum}`);
}
console.log(`Final sum: ${sum}`);
Python:
numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
sum_total = 0
print("Numbers:", numbers)
for number in numbers:
sum_total += number
print(f"Adding {number}, running total: {sum_total}")
print(f"Final sum: {sum_total}")
Classwork 1: Even Number Generator
Write a program that:
- Uses a for loop to print all even numbers from 2 to 20
- Calculates the sum of these even numbers
- Displays the final sum
Classwork 2: Countdown Timer
Create a countdown program:
- Start from 10 and count down to 1
- Display each number with “seconds remaining”
- Display “Blast off!” at the end
Classwork 3: Pattern Printer
Use nested for loops to print this pattern:
*
**
***
****
*****
Assignments
Assignment 1: Factorial Calculator Calculate the factorial of a number using a for loop:
- Input: A positive integer
- Calculate factorial (n! = 1 × 2 × 3 × … × n)
- Display the calculation process and final result
Assignment 2: Prime Number Finder Find all prime numbers between 1 and 50:
- Use nested loops to check if numbers are prime
- A prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself
- Display all prime numbers found
Assignment 3: Student Grade Processor Process grades for multiple students:
- Use a loop to input grades for 5 students
- Calculate each student’s average from 3 subjects
- Find and display the highest and lowest averages
Assignment 4: Pattern Generator Create a program that prints multiple patterns:
- Right triangle pattern with numbers
- Inverted triangle pattern
- Diamond pattern using stars Allow user to choose pattern type and size
Assignment 5: Sales Report Generator Generate a sales report for a week:
- Use a loop to input daily sales for 7 days
- Calculate total weekly sales
- Find the best and worst sales days
- Calculate average daily sales
- Display a formatted report
4. Arrays
Concept Overview
Arrays are data structures that can store multiple values in a single variable. They’re fundamental for organizing and manipulating collections of data.
Syntax Comparison
JavaScript:
// Array declaration and initialization
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let mixed = ["text", 42, true, null];
// Accessing elements (0-indexed)
console.log(fruits[0]); // "apple"
// Array methods
fruits.push("grape"); // Add to end
fruits.pop(); // Remove from end
fruits.unshift("mango"); // Add to beginning
fruits.shift(); // Remove from beginning
console.log(fruits.length); // Get array size
Java:
// Array declaration and initialization
String[] fruits = {"apple", "banana", "orange"};
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Accessing elements
System.out.println(fruits[0]); // "apple"
// Array length
System.out.println(fruits.length); // Get array size
// ArrayList for dynamic arrays
import java.util.ArrayList;
ArrayList<String> dynamicFruits = new ArrayList<>();
dynamicFruits.add("apple");
dynamicFruits.add("banana");
Python:
# List declaration and initialization
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
mixed = ["text", 42, True, None]
# Accessing elements
print(fruits[0]) # "apple"
print(fruits[-1]) # Last element: "orange"
# List methods
fruits.append("grape") # Add to end
fruits.pop() # Remove from end
fruits.insert(0, "mango") # Insert at position
fruits.remove("banana") # Remove by value
print(len(fruits)) # Get list size
Example 1: Shopping List Manager
JavaScript:
let shoppingList = ["milk", "bread", "eggs", "butter"];
console.log("Original shopping list:");
for (let i = 0; i < shoppingList.length; i++) {
console.log(`${i + 1}. ${shoppingList[i]}`);
}
// Add new items
shoppingList.push("cheese", "apples");
// Remove first item
shoppingList.shift();
console.log("\nUpdated shopping list:");
shoppingList.forEach((item, index) => {
console.log(`${index + 1}. ${item}`);
});
console.log(`\nTotal items: ${shoppingList.length}`);
Python:
shopping_list = ["milk", "bread", "eggs", "butter"]
print("Original shopping list:")
for i in range(len(shopping_list)):
print(f"{i + 1}. {shopping_list[i]}")
# Add new items
shopping_list.extend(["cheese", "apples"])
# Remove first item
shopping_list.pop(0)
print("\nUpdated shopping list:")
for index, item in enumerate(shopping_list):
print(f"{index + 1}. {item}")
print(f"\nTotal items: {len(shopping_list)}")
Example 2: Grade Analyzer
JavaScript:
let grades = [85, 92, 78, 96, 88, 73, 91];
console.log("All grades:", grades);
// Calculate average
let sum = 0;
for (let grade of grades) {
sum += grade;
}
let average = sum / grades.length;
// Find highest and lowest grades
let highest = Math.max(...grades);
let lowest = Math.min(...grades);
// Count grades by category
let aGrades = grades.filter(grade => grade >= 90).length;
let bGrades = grades.filter(grade => grade >= 80 && grade < 90).length;
console.log(`Average grade: ${average.toFixed(2)}`);
console.log(`Highest grade: ${highest}`);
console.log(`Lowest grade: ${lowest}`);
console.log(`A grades (90+): ${aGrades}`);
console.log(`B grades (80-89): ${bGrades}`);
Python:
grades = [85, 92, 78, 96, 88, 73, 91]
print("All grades:", grades)
# Calculate average
average = sum(grades) / len(grades)
# Find highest and lowest grades
highest = max(grades)
lowest = min(grades)
# Count grades by category
a_grades = len([g for g in grades if g >= 90])
b_grades = len([g for g in grades if 80 <= g < 90])
print(f"Average grade: {average:.2f}")
print(f"Highest grade: {highest}")
print(f"Lowest grade: {lowest}")
print(f"A grades (90+): {a_grades}")
print(f"B grades (80-89): {b_grades}")
Classwork 1: Number Array Operations
Create an array of 10 numbers and perform these operations:
- Calculate sum and average
- Find maximum and minimum values
- Count even and odd numbers
- Display results with appropriate labels
Classwork 2: Name List Manager
Create a program that manages a list of names:
- Start with an array of 5 names
- Add 2 more names to the end
- Remove the first name
- Sort the names alphabetically
- Display the final list with numbering
Classwork 3: Temperature Tracker
Create a temperature tracking system:
- Store daily temperatures for a week
- Calculate average temperature
- Find the hottest and coldest days
- Count days above and below average
Assignments
Assignment 1: Inventory Management System Create an inventory system for a store:
- Array of product names and corresponding quantities
- Functions to add new products, update quantities, and remove products
- Display current inventory with total items
- Find products that need restocking (quantity < 5)
Assignment 2: Student Test Score Analyzer Analyze test scores for a class:
- Array of student scores (at least 10 students)
- Calculate class average, median, and mode
- Determine grade distribution (A, B, C, D, F)
- Identify students above and below average
- Generate a complete statistical report
Assignment 3: Library Book Tracker Create a library book management system:
- Arrays for book titles, authors, and availability status
- Functions to check out books, return books, and search by title/author
- Display available books and checked-out books separately
- Calculate library utilization statistics
Assignment 4: Sales Performance Dashboard Track sales performance across different months:
- Array of monthly sales figures for a year
- Calculate quarterly totals and averages
- Identify best and worst performing months
- Calculate growth rate between consecutive months
- Generate performance trends and recommendations
Assignment 5: Game Score Leaderboard Create a leaderboard system for a game:
- Arrays for player names and their scores
- Functions to add new scores, update existing scores
- Sort players by score (highest to lowest)
- Display top 10 players
- Calculate average score and identify score ranges
- Implement score validation and duplicate handling
5. Array of JSON Objects
Concept Overview
Arrays of JSON objects combine the power of arrays with structured data. This pattern is extremely common in real-world applications for storing and manipulating complex data like user profiles, product catalogs, or database records.
Syntax Comparison
JavaScript:
// Array of JSON objects
let students = [
{
id: 1,
name: "Alice Johnson",
age: 20,
grades: [85, 92, 78],
isActive: true
},
{
id: 2,
name: "Bob Smith",
age: 22,
grades: [90, 88, 94],
isActive: false
}
];
// Accessing data
console.log(students[0].name); // "Alice Johnson"
console.log(students[1].grades[0]); // 90
// Array methods for objects
let activeStudents = students.filter(student => student.isActive);
let names = students.map(student => student.name);
Java:
// Using ArrayList with custom class or HashMap
import java.util.*;
// Method 1: Using HashMap
List<Map<String, Object>> students = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, Object> student1 = new HashMap<>();
student1.put("id", 1);
student1.put("name", "Alice Johnson");
student1.put("age", 20);
student1.put("grades", Arrays.asList(85, 92, 78));
students.add(student1);
// Method 2: Custom class (recommended)
public class Student {
int id;
String name;
int age;
List<Integer> grades;
boolean isActive;
}
Python:
# List of dictionaries
students = [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Alice Johnson",
"age": 20,
"grades": [85, 92, 78],
"is_active": True
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Bob Smith",
"age": 22,
"grades": [90, 88, 94],
"is_active": False
}
]
# Accessing data
print(students[0]["name"]) # "Alice Johnson"
print(students[1]["grades"][0]) # 90
# List comprehensions for filtering/mapping
active_students = [s for s in students if s["is_active"]]
names = [student["name"] for student in students]
Node.js:
// Same as JavaScript, but often with additional JSON operations
const fs = require('fs');
// Reading JSON from file
let studentsData = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync('students.json', 'utf8'));
// Writing JSON to file
fs.writeFileSync('output.json', JSON.stringify(students, null, 2));
Example 1: Employee Management System
JavaScript:
let employees = [
{
id: 101,
name: "Sarah Wilson",
department: "Engineering",
salary: 75000,
skills: ["JavaScript", "Python", "React"],
startDate: "2022-03-15"
},
{
id: 102,
name: "Mike Chen",
department: "Marketing",
salary: 55000,
skills: ["SEO", "Analytics", "Content Writing"],
startDate: "2023-01-20"
},
{
id: 103,
name: "Lisa Rodriguez",
department: "Engineering",
salary: 80000,
skills: ["Java", "Spring", "AWS"],
startDate: "2021-11-08"
}
];
console.log("=== EMPLOYEE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ===");
// Display all employees
console.log("\nAll Employees:");
employees.forEach(emp => {
console.log(`ID: ${emp.id} | ${emp.name} | ${emp.department} | $${emp.salary}`);
});
// Filter engineers
let engineers = employees.filter(emp => emp.department === "Engineering");
console.log(`\nEngineers: ${engineers.length}`);
// Calculate average salary
let totalSalary = employees.reduce((sum, emp) => sum + emp.salary, 0);
let avgSalary = totalSalary / employees.length;
console.log(`Average Salary: $${avgSalary.toFixed(2)}`);
// Find employees with specific skills
let jsEmployees = employees.filter(emp => emp.skills.includes("JavaScript"));
console.log(`\nJavaScript Developers: ${jsEmployees.map(emp => emp.name).join(", ")}`);
Python:
employees = [
{
"id": 101,
"name": "Sarah Wilson",
"department": "Engineering",
"salary": 75000,
"skills": ["JavaScript", "Python", "React"],
"start_date": "2022-03-15"
},
{
"id": 102,
"name": "Mike Chen",
"department": "Marketing",
"salary": 55000,
"skills": ["SEO", "Analytics", "Content Writing"],
"start_date": "2023-01-20"
},
{
"id": 103,
"name": "Lisa Rodriguez",
"department": "Engineering",
"salary": 80000,
"skills": ["Java", "Spring", "AWS"],
"start_date": "2021-11-08"
}
]
print("=== EMPLOYEE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ===")
# Display all employees
print("\nAll Employees:")
for emp in employees:
print(f"ID: {emp['id']} | {emp['name']} | {emp['department']} | ${emp['salary']}")
# Filter engineers
engineers = [emp for emp in employees if emp["department"] == "Engineering"]
print(f"\nEngineers: {len(engineers)}")
# Calculate average salary
total_salary = sum(emp["salary"] for emp in employees)
avg_salary = total_salary / len(employees)
print(f"Average Salary: ${avg_salary:.2f}")
# Find employees with specific skills
js_employees = [emp for emp in employees if "JavaScript" in emp["skills"]]
js_names = [emp["name"] for emp in js_employees]
print(f"\nJavaScript Developers: {', '.join(js_names)}")
Example 2: Product Catalog
JavaScript:
let products = [
{
id: "P001",
name: "Laptop",
category: "Electronics",
price: 999.99,
stock: 15,
tags: ["computer", "portable", "work"],
specifications: {
brand: "TechBrand",
model: "Pro X1",
warranty: "2 years"
}
},
{
id: "P002",
name: "Coffee Maker",
category: "Appliances",
price: 79.99,
stock: 8,
tags: ["kitchen", "coffee", "morning"],
specifications: {
brand: "BrewMaster",
capacity: "12 cups",
warranty: "1 year"
}
},
{
id: "P003",
name: "Running Shoes",
category: "Sports",
price: 129.99,
stock: 0,
tags: ["shoes", "running", "fitness"],
specifications: {
brand: "RunFast",
size: "Various",
warranty: "6 months"
}
}
];
console.log("=== PRODUCT CATALOG ===");
// Display available products (in stock)
let availableProducts = products.filter(p => p.stock > 0);
console.log("\nAvailable Products:");
availableProducts.forEach(product => {
console.log(`${product.name} - $${product.price} (Stock: ${product.stock})`);
});
// Products by category
let categories = [...new Set(products.map(p => p.category))];
console.log("\nProducts by Category:");
categories.forEach(category => {
let categoryProducts = products.filter(p => p.category === category);
console.log(`${category}: ${categoryProducts.length} products`);
});
// Find products in price range
let budgetProducts = products.filter(p => p.price < 100);
console.log(`\nProducts under $100: ${budgetProducts.length}`);
// Search by tag
function searchByTag(tag) {
return products.filter(p => p.tags.includes(tag));
}
let kitchenProducts = searchByTag("kitchen");
console.log(`\nKitchen products: ${kitchenProducts.map(p => p.name).join(", ")}`);
Classwork 1: Student Grade Book
Create a student gradebook system with JSON objects:
- Each student object should have: id, name, class, grades array, attendance
- Calculate each student’s average grade
- Find students with perfect attendance
- Identify students who need academic support (average < 70)
Classwork 2: Library Book Database
Design a library system:
- Each book object: id, title, author, genre, isCheckedOut, dueDate
- Find all available books
- Group books by genre
- Track overdue books
- Display checkout statistics
Classwork 3: Restaurant Menu System
Create a restaurant menu management system:
- Each item object: id, name, category, price, ingredients, isVegetarian
- Filter items by dietary preferences
- Calculate total menu value
- Find most expensive items in each category
Assignments
Assignment 1: E-commerce Order Management Build an order management system:
- Order objects with: orderId, customerId, items array, totalAmount, status, orderDate
- Item objects with: productId, name, quantity, price
- Calculate monthly sales totals
- Find top customers by order value
- Track order status distribution
- Generate sales reports by product
Assignment 2: Hospital Patient Management Create a patient management system:
- Patient objects: patientId, name, age, admissionDate, department, doctor, treatments array, discharged
- Treatment objects: treatmentId, type, date, cost, notes
- Calculate total treatment costs per patient
- Find patients by department or doctor
- Track average length of stay
- Generate billing reports and patient statistics
Assignment 3: Social Media Analytics Dashboard Build a social media analytics system:
- Post objects: postId, userId, content, timestamp, likes, shares, comments array
- User objects: userId, username, followers, following, postsCount
- Comment objects: commentId, userId, content, timestamp, likes
- Calculate engagement rates for posts
- Find trending posts (high engagement)
- Analyze user activity patterns
- Generate content performance reports
Assignment 4: School Management System Design a comprehensive school management system:
- Student objects: studentId, name, grade, subjects array, grades, attendance, guardian info
- Teacher objects: teacherId, name, subjects, classes, experience
- Class objects: classId, subject, teacher, students, schedule, room
- Calculate class averages and teacher workloads
- Track attendance patterns across grades
- Generate report cards and academic analytics
- Identify students needing additional support
Assignment 5: Inventory and Sales Analytics Create an advanced inventory and sales system:
- Product objects: productId, name, category, supplier, cost, sellPrice, stock, reorderLevel
- Sale objects: saleId, productId, quantity, date, customerId, totalAmount, discount
- Supplier objects: supplierId, name, contact, reliability rating, products array
- Track inventory levels and automatic reorder alerts
- Calculate profit margins and best-selling products
- Analyze seasonal sales trends
- Generate comprehensive business intelligence reports
Learning Path Recommendations
Beginner Level (Weeks 1-2)
- Master basic syntax and variables in your chosen language
- Practice if-else statements with simple decision-making programs
- Learn for loops with counting and simple iterations
Intermediate Level (Weeks 3-4)
- Work extensively with arrays and basic data manipulation
- Combine loops with arrays for data processing
- Start simple JSON object operations
Advanced Level (Weeks 5-6)
- Master arrays of JSON objects
- Build complete applications combining all concepts
- Focus on real-world problem solving
Practice Tips
- Start Small: Begin with simple examples before moving to complex assignments
- Code Daily: Consistent practice is more effective than long sessions
- Debug Actively: Learn to read and fix error messages
- Experiment: Modify examples to see how changes affect output
- Build Projects: Apply concepts to create useful applications
Language-Specific Resources
- JavaScript: Focus on ES6+ features, async operations, DOM manipulation
- Python: Explore libraries like pandas for data analysis, Flask for web apps
- Java: Learn object-oriented concepts, Spring framework basics
- Node.js: Understand npm packages, Express.js, API development
Assessment Criteria
For each assignment, evaluate:
- Correctness: Does the code work as intended?
- Efficiency: Is the solution optimized for performance?
- Readability: Is the code well-structured and commented?
- Problem-solving: Does it handle edge cases and errors?
- Creativity: Are there innovative approaches to the solution?
Additional Challenges
Cross-Language Migration
Once comfortable with one language, try implementing the same solutions in other languages to understand:
- Syntax differences
- Language-specific features
- Performance characteristics
- Best practices per language
Real-World Applications
Apply these concepts to build:
- Web applications (JavaScript/Node.js)
- Data analysis tools (Python)
- Desktop applications (Java)
- Mobile app backends (Node.js)
- Automation scripts (Python)
Next Steps
After mastering these fundamentals, explore:
- Object-Oriented Programming (Classes, Inheritance)
- Database interactions (SQL, NoSQL)
- Web development frameworks
- API development and consumption
- Testing and debugging techniques
- Version control with Git
Conclusion
This curriculum provides a solid foundation in programming fundamentals across multiple languages. The progression from basic variables to complex data structures prepares students for real-world development challenges. Remember that programming is learned through practice—the more you code, the more natural these concepts become.
Each concept builds upon the previous ones, so ensure mastery of each level before advancing. The assignments are designed to reinforce learning through practical application, preparing you for professional software development challenges.