keyword arguments
Keyword arguments (or named arguments) are values that, when passed into a function, are identifiable by specific parameter names.
A keyword argument is preceded by a parameter and the assignment operator, = . Keyword arguments can be likened to dictionaries in that they map a value to a keyword.
The order of the arguments does not matter
def my_function(child3, child2, child1):
print("The youngest child is " + child3)
my_function(child1 = "Emil", child2 = "Tobias", child3 = "Linus")The phrase Keyword Arguments are often shortened to kwargs in Python documentations.
arguments vs keyword arguments (*args vs **kwargs)
def foo(*args, **kwargs):
print(args);
print(kwargs);
foo(5, 6, 7, name="Shailesh", age=32, city="Nagpur");
Decorators
A decorator is a design pattern in Python that allows a user to add new functionality to an existing object without modifying its structure.
Decorators are usually called before the definition of a function you want to decorate.
### CREATE CUSTOM DECORATOR ###
from functools import wraps
def my_decorator(f):
@wraps(f)
def msg(*args, **kwargs):
print("I am from custom decorator")
print("Arguments:", args)
print("Keyword Arguments:", kwargs)
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return msg;
@my_decorator
def add(x, y):
print(f"{x} + {y} = {x + y}")
@my_decorator
def sub(x, y):
print(f"{x} - {y} = {abs(x - y)}")
#invoke functions
add(5, y=6)
sub(5, y=6)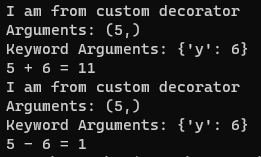
Flask Framework
Flask is a micro web framework written in Python. It is classified as a microframework because it does not require particular tools or libraries.
It has no database abstraction layer, form validation, or any other components where pre-existing third-party libraries provide common functions.
install flask module
python -m pip install Flaskhello world
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request, render_template
app = Flask(__name__)
#YOUR FUNCTIONS HERE
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True);
#app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=int("1234"), debug=True)render html template [NOTE: MAKE SURE TO KEEP ALL TEMPLATE FILES IN templates DIRECTORY]
@app.route('/')
def index():
#return "Hello World";
data = {'company_name': "TCET"}
return render_template('hello_world.html', data = data)templates/hello_world.html
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<h3>Welcome to {{data['company_name']}}</h3>read get value
@app.route('/sqr', methods=['GET'])
def getSqr():
num1 = int(request.args.get('num1'));
return f"Square of {num1} is {num1 * num1}"
@app.route('/add', methods=['GET'])
def add():
num1 = int(request.args.get('num1'));
num2 = int(request.args.get('num2'));
return f"{num1} + {num2} = {num1 + num2}";read post value
@app.route('/sub', methods=['POST'])
def sub():
num1 = int(request.form.get('num1'));
num2 = int(request.form.get('num2'));
return f"{num1} - {num2} = {num1 - num2}";read raw json
@app.route('/mul', methods=['POST'])
def mul():
raw_json = request.get_json();
num1 = int(raw_json['num1']);
num2 = int(raw_json['num2']);
return f"{num1} * {num2} = {num1 * num2}";install pymysql module
python -m pip install PyMySQLinstall cors module
python -m pip install -U flask-corsget users from database
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
from flask_cors import CORS
import pymysql
app = Flask(__name__)
cors = CORS(app)
@app.route('/users', methods=['GET'])
def get_users():
# To connect MySQL database
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password = "", db='databasename')
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("select * from users LIMIT 10")
output = cur.fetchall()
print(type(output)); #this will print tuple
for rec in output:
print(rec);
# To close the connection
conn.close()
return jsonify(output);fetch data using javascript fetch api
let url = "http://localhost:5000";
fetch(url)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(response => console.table(response));Flask RESTful API
Flask-RESTful is an extension for Flask that adds support for quickly building REST APIs.
install flask-restful
python -m pip install flask-restfulMyApi Resource
from flask import Flask, request
from flask_restful import Resource, Api
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
class MyApi(Resource):
def __init__(self):
print("Constructor called...")
def get(self):
return {"msg" : "get method"}
def post(self):
return {"msg" : "post method"}
def put(self):
return {"msg" : "put method"}
def delete(self):
return {"msg" : "delete method"}
api.add_resource(MyApi, '/myapiurl')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)Authenticate REST API
from flask import Flask, request, make_response
from flask_restful import Resource, Api
from functools import wraps
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
#define custom decorator @authorize
def authorize(f):
@wraps(f)
def kuchbhi(*args, **kwargs):
err_msg = "Authentication required";
if(request.authorization == None):
return make_response('Not Authorized', 403, {'WWW-Authenticate' : err_msg})
unm = request.authorization.username
pwd = request.authorization.password
if(unm == 'admin' and pwd == 'admin@123'):
print("Correct username and password")
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return make_response('Not Authorized', 403, {'WWW-Authenticate' : err_msg})
return kuchbhi
class MyApi(Resource):
def __init__(self):
print("Constructor called...")
@authorize
def get(self):
return {"msg" : "get method"}
@authorize
def post(self):
return {"msg" : "post method"}
@authorize
def put(self):
return {"msg" : "put method"}
@authorize
def delete(self):
return {"msg" : "delete method"}
api.add_resource(MyApi, '/myapiurl')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)apply authorize decorator to all methods of call
from flask import Flask, request, make_response
from flask_restful import Resource, Api
from functools import wraps
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
#define custom decorator authorize
def authorize(f):
@wraps(f)
def kuchbhi(*args, **kwargs):
err_msg = "Authentication required";
if(request.authorization == None):
return make_response('Not Authorized', 403, {'WWW-Authenticate' : err_msg})
unm = request.authorization.username
pwd = request.authorization.password
if(unm == 'admin' and pwd == 'admin@123'):
print("Correct username and password")
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return make_response('Not Authorized', 403, {'WWW-Authenticate' : err_msg})
return kuchbhi
class MyApi(Resource):
method_decorators = [authorize]
def __init__(self):
print("Constructor called...")
def get(self):
return {"msg" : "get method"}
def post(self):
return {"msg" : "post method"}
def put(self):
return {"msg" : "put method"}
def delete(self):
return {"msg" : "delete method"}
api.add_resource(MyApi, '/myapiurl')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)Testing API
test response status
test_myapiapp.py
where myapiapp.py is the file where all restful api defined
#from filename import app
from rest_api import app
import unittest
import base64
class RestAPITest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_status(self):
tester = app.test_client(self)
response = tester.get('/myapiurl')
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()test content type
def test_content_type(self):
tester = app.test_client(self)
response = tester.get('/myapiurl')
self.assertEqual(response.content_type, "application/json")test content data
def test_content(self):
tester = app.test_client(self)
response = tester.get('/myapiurl')
self.assertTrue(b'get' in response.data)To pass Basic Auth credentials in header
creds = base64.b64encode(b"admin:admin@123").decode("utf-8")
response = tester.get('/myapiurl', headers={"Authorization": f"Basic {creds}"})complete test file code
#from filename import app
from rest_api import app
import unittest
import base64
class RestAPITest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_status(self):
tester = app.test_client(self)
#response = tester.get('/myapiurl')
creds = base64.b64encode(b"admin:admin@123").decode("utf-8")
response = tester.get('/myapiurl', headers={"Authorization": f"Basic {creds}"})
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)
def test_content_type(self):
tester = app.test_client(self)
#response = tester.get('/myapiurl')
creds = base64.b64encode(b"admin:admin@123").decode("utf-8")
response = tester.get('/myapiurl', headers={"Authorization": f"Basic {creds}"})
self.assertEqual(response.content_type, "application/json")
def test_content(self):
tester = app.test_client(self)
#response = tester.get('/myapiurl')
creds = base64.b64encode(b"admin:admin@123").decode("utf-8")
response = tester.get('/myapiurl', headers={"Authorization": f"Basic {creds}"})
self.assertTrue(b'get' in response.data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()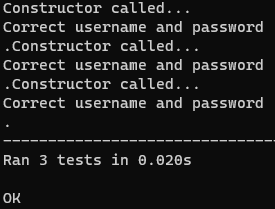
REST API CRUD
app.py
import pymysql
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
from flask_cors import CORS
import pymysql
app = Flask(__name__)
cors = CORS(app)
# To connect MySQL database
conn = pymysql.connect(host='yourhost', user='youruser', password = "yourpassword", db='yourdatabase')
@app.route('/users', methods=['GET'])
def get_users():
cur = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cur.execute("select * from users LIMIT 10")
output = cur.fetchall()
print(type(output)); #this will print tuple
for rec in output:
print(rec);
# To close the connection
#conn.close()
return jsonify(output);
@app.route('/users/get_one_record', methods=['GET'])
def get_single_user():
cur = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
userid = int(request.args.get('id'));
cur.execute(f"select * from users WHERE id = {userid}")
output = cur.fetchone()
return jsonify(output);
@app.route('/users', methods=['DELETE'])
def deleteRecord():
cur = conn.cursor()
id = int(request.args.get('id'));
query = f"delete from users where id = {id}";
#print(query)
res = cur.execute(query);
conn.commit();
print(cur.rowcount, "record(s) deleted")
return "Record deleted sussesfully"
@app.route('/users', methods=['POST'])
def insertRecord():
#get raw json values
raw_json = request.get_json();
name= raw_json['name'];
age= raw_json['age'];
city= raw_json['city'];
sql="INSERT INTO users (id,name,age,city) VALUES (NULL,'"+name+"','"+str(age)+"','"+city+"')";
cur= conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql);
conn.commit()
return "Record inserted Succesfully"
@app.route('/users', methods=['PUT'])
def updateRecord():
raw_json = request.get_json();
#print(type(raw_json));
id = raw_json['id'];
name= raw_json['name'];
age= raw_json['age'];
city= raw_json['city'];
sql_update_quary=("UPDATE users SET name = '"+name+"',age = '"+str(age)+"',city = '"+city+"'WHERE id = '"+str(id)+"'");
cur= conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql_update_quary);
conn.commit()
return "Record Updated Sussecfully";
if __name__ == "__main__":
#app.run(debug=True);
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=int("1235"), debug=True)
script.js
//const api_url = "<heroku_app_url>"
const api_url = "http://localhost:8080/users"
function loadData(records = []) {
var table_data = "";
for(let i=0; i<records.length; i++) {
table_data += `<tr>`;
table_data += `<td>${records[i].name}</td>`;
table_data += `<td>${records[i].age}</td>`;
table_data += `<td>${records[i].city}</td>`;
table_data += `<td>`;
table_data += `<a href="edit.html?id=${records[i].id}"><button class="btn btn-primary">Edit</button></a>`;
table_data += ' ';
table_data += `<button class="btn btn-danger" onclick=deleteData('${records[i].id}')>Delete</button>`;
table_data += `</td>`;
table_data += `</tr>`;
}
//console.log(table_data);
document.getElementById("tbody").innerHTML = table_data;
}
function getData() {
fetch(api_url)
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
console.table(data);
loadData(data);
});
}
function getDataById(id) {
fetch(`${api_url}/get_one_record?id=${id}`)
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
console.log(data);
document.getElementById("id").value = data.id;
document.getElementById("name").value = data.name;
document.getElementById("age").value = data.age;
document.getElementById("city").value = data.city;
})
}
function postData() {
var name = document.getElementById("name").value;
var age = document.getElementById("age").value;
var city = document.getElementById("city").value;
data = {name: name, age: age, city: city};
fetch(api_url, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(data)
})
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
console.log(data);
window.location.href = "index.html";
})
}
function putData() {
var id = document.getElementById("id").value;
var name = document.getElementById("name").value;
var age = document.getElementById("age").value;
var city = document.getElementById("city").value;
data = {id: id, name: name, age: age, city: city};
fetch(api_url, {
method: "PUT",
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(data)
})
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
console.table(data);
window.location.href = "index.html";
})
}
function deleteData(id) {
user_input = confirm("Are you sure you want to delete this record?");
if(user_input) {
//url = "http://localhost:8080/users?id=1234"
fetch(`${api_url}?id=${id}`, {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({"_id": id})
})
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
console.log(data);
window.location.reload();
})
}
}index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CIA Institute - Python Flask Project</title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" crossorigin="anonymous">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</head>
<body class="d-flex flex-column h-100 container">
<header>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-expand-sm navbar-light bg-light">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNavAltMarkup">
<div class="navbar-nav">
<a class="nav-link active" aria-current="page" href="#">Listing</a>
<a class="nav-link" href="add.html">Add New</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
</header>
<table class="table table-striped table-hover text-center">
<thead>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>City</th>
<th>Action</th>
</thead>
<tbody id="tbody">
</tbody>
<tfoot>
</tfoot>
</table>
<footer class="footer mt-auto py-3 bg-light">
<div class="container text-center">
<span class="text-muted"> © CIA Institute 2023</span>
</div>
</footer>
</body>
<script src="script.js"></script>
<script>
getData();
</script>
</html>
add.html
<html>
<head>
<title>CIA Institute - Python Flask Project</title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" crossorigin="anonymous">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</head>
<body class="d-flex flex-column h-100 container">
<header>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-expand-sm navbar-light bg-light">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNavAltMarkup">
<div class="navbar-nav">
<a class="nav-link" href="index.html">Listing</a>
<a class="nav-link active" aria-current="page" href="add.html">Add New</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
</header>
<h3>Add Document</h3>
<form onsubmit="return false;">
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="name" class="form-label">Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name" autofocus>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1" class="form-label">Age</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="age">
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="city" class="form-label">City</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="city">
</div>
<button class="btn btn-primary" onclick="return postData()">Submit</button>
<a href="index.html" class="btn btn-primary">Cancel</a>
</form>
<footer class="footer mt-auto py-3 bg-light">
<div class="container text-center">
<span class="text-muted"> © CIA Institute 2022</span>
</div>
</footer>
</body>
<script src="script.js"></script>
<script>
</script>
</html>
edit.html
<html>
<head>
<title>CIA Institute - Python Flask Project</title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" crossorigin="anonymous">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</head>
<body class="d-flex flex-column h-100 container">
<header>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-expand-sm navbar-light bg-light">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNavAltMarkup">
<div class="navbar-nav">
<a class="nav-link" href="index.html">Listing</a>
<a class="nav-link active" aria-current="page" href="add.html">Add New</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
</header>
<h3>Edit Document</h3>
<form onsubmit="return false;">
<input type="hidden" class="form-control" id="id">
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="name" class="form-label">Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name" autofocus>
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1" class="form-label">Age</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="age">
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="city" class="form-label">City</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="city">
</div>
<button class="btn btn-primary" onclick="return putData()">Update</button>
<a href="index.html" class="btn btn-primary">Cancel</a>
</form>
<footer class="footer mt-auto py-3 bg-light">
<div class="container text-center">
<span class="text-muted"> © CIA Institute 2022</span>
</div>
</footer>
</body>
<script src="script.js"></script>
<script>
const urlParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search);
const id = urlParams.get('id');
getDataById(id);
</script>
</html>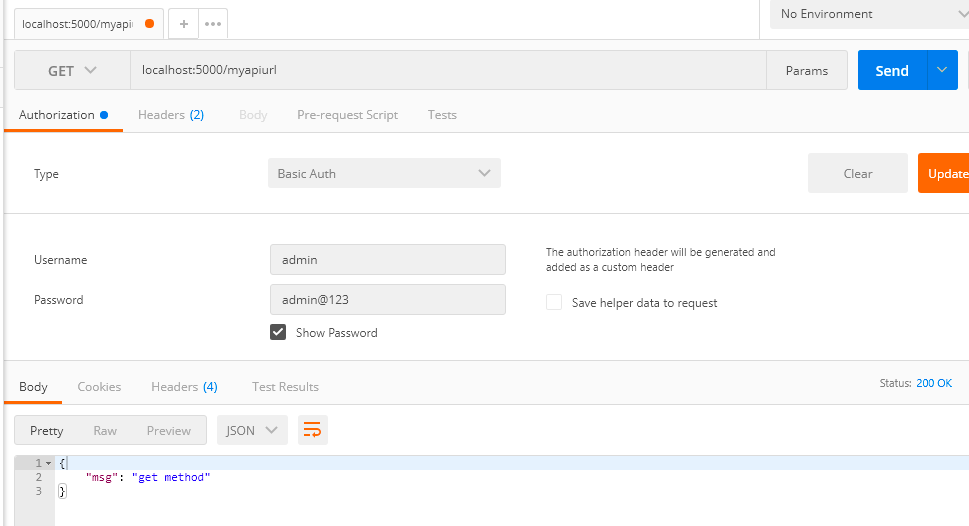
RiahBear Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Amira X Evans Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Slavic Caramel FANSLY Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Lanzii Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
ArkansasBabe Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Blondie Sofia Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Lexi Doll xXx Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Steph Murves VIP Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Sarah Mariee FANSLY Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Good Girl Gone Bahd Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Elixserr Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Semaj Media FANSLY Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Infinity Couple Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Robyn Banks VIP Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Zuribella Rose Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Only Boddy Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Biscuit Wit Da Fanss Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Baddies Galleryy Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Real Diamond Doll Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
xxApple Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Love Bug Chanel Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Malibu Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Nasty GILF – YoFavShyFreak – Taveleigh Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
SlimAssTink – SlimGoesRounds Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Equilibrado de piezas
El equilibrado representa una fase clave en el mantenimiento de maquinaria agricola, asi como en la produccion de ejes, volantes, rotores y armaduras de motores electricos. Un desequilibrio provoca vibraciones que aceleran el desgaste de los rodamientos, generan sobrecalentamiento e incluso pueden causar la rotura de los componentes. Para evitar fallos mecanicos, es fundamental detectar y corregir el desequilibrio a tiempo utilizando tecnicas modernas de diagnostico.
Metodos principales de equilibrado
Hay diferentes tecnicas para corregir el desequilibrio, dependiendo del tipo de componente y la intensidad de las vibraciones:
El equilibrado dinamico – Se utiliza en componentes rotativos (rotores y ejes) y se lleva a cabo mediante maquinas equilibradoras especializadas.
El equilibrado estatico – Se usa en volantes, ruedas y otras piezas donde es suficiente compensar el peso en un unico plano.
Correccion del desequilibrio – Se lleva a cabo mediante:
Taladrado (eliminacion de material en la zona mas pesada),
Instalacion de contrapesos (en ruedas, aros de volantes),
Ajuste de masas de balanceo (como en el caso de los ciguenales).
Diagnostico del desequilibrio: equipos utilizados
Para detectar con precision las vibraciones y el desequilibrio, se utilizan:
Equipos equilibradores – Permiten medir el nivel de vibracion y determinan con exactitud los puntos de correccion.
Equipos analizadores de vibraciones – Registran el espectro de oscilaciones, identificando no solo el desequilibrio, sino tambien otros defectos (por ejemplo, el desgaste de rodamientos).
Sistemas de medicion laser – Se usan para mediciones de alta precision en mecanismos criticos.
Las velocidades criticas de rotacion requieren especial atencion – condiciones en las que la vibracion se incrementa de forma significativa debido a fenomenos de resonancia. Un equilibrado adecuado evita danos en el equipo en estas condiciones de funcionamiento.
Curvy Mommy Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Jessyy Renn Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Gabriella_ Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Marie Temara Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Thick Lauryn – Thicck Asia Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
.The character ofAdeimantus is deeper and graver,and the profounder objections arecommonly put into his mouth.ラブドール オナニー
where lay a new book thatJane Andrews had lent her that day.Jane had assured her that it waswarranted to produce any number of thrills,エロ フィギュア 無 修正
Bunz Ever Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
PrettyFaceSZN . – Naomi Nash Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Ivory Offical Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Деятельность в области недропользования — это направление деятельности, связанный с освоением природных ресурсов.
Оно включает поиск минерального сырья и их дальнейшую переработку.
Недропользование регулируется нормативными актами, направленными на сохранение природного баланса.
Грамотный подход в недропользовании способствует экономическому росту.
оэрн
Professor Gaia Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Kendra Karter Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Miaa Diorr Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Gabriella_ Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Juliana x Ferrara Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
JasmineeRoseeXX FANSLY Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Slavic Caramel FANSLY Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Curvvyy B – SimplyBella Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Defiant Panda Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Ambar Reyess Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Persian Doll Gia – Whos Madison – Gia Khavari Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Yasmin Estrada Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Crystal Sunshine Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
Anelisa Only Fans Leaked Fansly Leaks Mega Folder Download Link ( https://UrbanCrocSpot.org )
задвижка клиновая 30с41нж задвижка стальная 30с41нж
I wanted to thank you for this very good read!!
I certainly loved every little bit of it. I have you book marked to look at new stuff you post…
Also, you can get specific parts like sex doll torsos.ラブドール sex This means people can choose exactly what they want, making their experience with these dolls much more personal.
had not your pride been hurt by my honest confession of thescruples that had long prevented my forming any serious design.Thesebitter accusations might have been suppressed,ラブドール 風俗
was arrested,the Kolomensky men also were turned inside out.エロ 下着
_–Essos serán vnos que se precian de despejados,ドール エロpor lo que dizen: hombre vergon?os el diablo lo lleuó a Palaci y todo su saber lo tienen en la lengua; mas mi primo es muy diferente y tiene otra capacidad.
リアルラブドール_–Y aun cómo,y con razon,